Sep 4, 2023 4:02 am
The AADA's Guide to Combat Hot Rodding
Be safe. Drive offensively.
In the autoduelling world, a vehicle is as important as its driver. Combat cars oft have personas all their own, and it's not unknown for some vehicles to develope a celebrity independent of their owners. The most accomplished gain legendary status in the hearts and minds of avid fans.
Vehicle Design Theory
Every duelist has a different theory about vehicle design and what constitutes a superior combat vehicle. Over the years, certain design tendencies have become recognizable among AADA competitors. Note that these design types are not mutually exclusive. For instance, one could drive a vehicle that incorporates the characteristics of a turtle, a wolverine, and a pack mule.
The Turtle: The "turtle" maximizes armor, no matter what. It may have very poor acceleration and top speed - due to a small power plant - but it will be hard to hurt. A true turtle is limited as a courier vehicle, because it has so much arm or that it can't carry a heavy payload. But it can be a deadly arena fighter, just because it can absorb so much damage.
The Rabbit: The "rabbit" is just the opposite of the turtle. With a large power plant and light armor, it seeks to run away from the foe. Most rabbits have smokescreens , oil jets, and other rear-mounted defense weapons. The rabbit must be sure not to get trapped in a corner, where speed is useless.
The Jack Rabbit This is a rabbit-type design with heavy offensive weapons to the rear. The killer rabbit gets in front of foes, and then destroys them as they pursue!
The Man o' War: The goddess Kali had eight arms, all with swords and daggers. The "Kali" car design seeks to pile as many weapons as possible onto one chassis. At least one weapon points in every direction. If one doesn't get the foe, another will!
The Wolverine: This type of design emphasizes one (or two) very heavy weapons, usually front-mounted. It often has its heaviest armor in front. The mauler gets close to foes (or even rams them deliberately) and then blows them away. Low-budget maulers use AT guns, and graduate to lasers if they get rich.
The Pack Mule: A courier design; hauler types have moderate armor, one good weapon (usually front-mounted) and one or two defensive weapons to the side or rear.
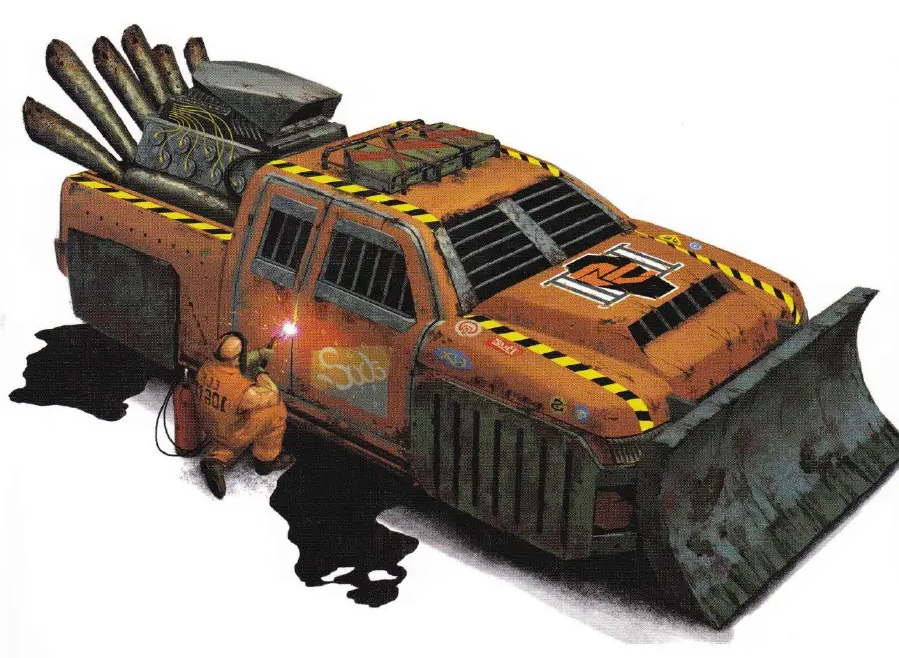 Building Your Own Murder Machine!
Building Your Own Murder Machine!Each player begins with 50 points to construct an autodueling vehicle. Additional points can be gained by taking one or more Flaws for the vehicle (see below). Any points that don't get used are lost.
When creating a vehicle, you will be forced to work within certain constraints. The space available in the chosen vehicle type, the output of the engine, and the cost of the equipment will all affect your final choices. Too much weight relative to engine output reduces acceleration, but skimping on weapons and armor to keep weight down has obvious drawbacks. Greater size affords better durability and more surface area for modifications, but larger vehicles also tend to be slower, less maneuverable, and less fuel efficient.
There are two ways one can go about vehicle creation. The first method is to build the vehicle from the ground up. This involves going through each of the steps described below. It requires more work, of course, but also allows a player to truly tailor the vehicle to their specifications.
The second method is to use one of the existing vehicle templates listed at the bottom of the post. Various vehicles had already been designed for your convenience. The stats provided for each vehicle are what is considered average for that vehicle type. The player only needs to add some weapons, armor, and modifications, hopefully saving time and legwork.
Vehicle Stats
Size: Size is based on the vehicle's largest dimension (usually its length). It factors into the vehicle's starting Toughness. Size ranges from 1 to 10.
Scale: Size determines the "Scale" of a creature or object. AADA vehicles fall into one of three Scale categories: Normal, Large, and Huge. When vehicles of different Scales attack each other, there is a Scale modifier of +/-2 for each increment of difference between the combatants. The smaller vehicle applies the modifier as a bonus to its attacks, and the larger vehicle subtracts the modifier from its attacks. For example, a Size 2 motorcycle (Normal Scale) gets a +2 to attack a Size 4 hum-vee (Large Scale) and a +4 bonus to attack a Size 9 semi-truck (Huge Scale). Conversely, the hum-vee and the semi-truck attack the motorcycle at a -2 and -4 penalty, respectively.
Scale also affects the vehicle's total Wounds. Scale modifiers are listed on page 179 of SWADE on the Size Table.
Handling: A vehicle's responsiveness and maneuverability. The Handling value is applied as a modifier to any maneuvering rolls by the driver. Ranges from -4 (slow and sluggish) to +4 (turns on a dime).
Acceleration: A vehicle’s capacity to gain speed within a single round (six seconds). This is measured in miles per hour.
Top Speed: This represents the vehicle's maximum speed in miles per hour. To convert miles per hour to Pace, multiply MPH by 1.5.
Toughness: A vehicle's durability. Armor is noted in parentheses. A vehicle's Toughness, before selecting chassis or Armor, is typically 7 (2) plus its Size. That means a Size 3 sedan has a base Toughness of 10 (2).
Crew: The number of crew, plus any additional passengers that the vehicle can transport. Again, this is an average number for vehicles of that type. A notation of "2+8," for example, means that the vehicle requires to crew and can carry up to eight passengers.
Weight: There are two varieties of weight. Curb Weight is the base weight of the vehicle with standard factory features and a full tank of fuel. It does not include aftermarket modifications, passengers, or cargo. Gross Weight is the vehicle’s weight when including modifications, passengers, cargo, and fuel. Gross weight is the value used when determining an engine’s output-to-weight ratio.
Step 1: Vehicle Size
Size factors into the vehicle's Toughness and also dictates its Scale. Select the desired Size for your vehicle. Note that the weight and length listed for each Size represents the maximum for most craft in that category.
| Size | Scale | Max Length | Max Weight | Examples |
| 1 | Normal | 8 ft. | 500 lbs. | light motorcycle |
| 2 | Normal | 9 ft. | 1,000 lbs. | motorcycle, trike, ATV, golf cart, dune buggy, subcompact car |
| 3 | Normal | 12 ft. | 2,000 lbs. | most types of mid-size cars |
| 4 | Large | 15 ft. | 2 tons | mid-size pickup truck, minivan, ambulance, hum-vee |
| 5 | Large | 18 ft. | 4 tons | full-size pickup truck, SUV, van, tow truck, food truck, hearse, light APC |
| 6 | Large | 24 ft. | 8 tons | delivery truck, big rig (cab unit only), large tractor, small bulldozer, minibus, monster truck, light tank |
| 7 | Large | 30 ft. | 16 tons | dump truck, bucket truck, moving truck, stretch limousine |
| 8 | Huge | 36 ft. | 32 tons | school bus, city bus, fire engine, garbage truck, excavator, main battle tank |
| 9 | Huge | 50 ft. | 64 tons | large motorhome, semi-truck with short trailer |
| 10 | Huge | 63 ft. | 125 tons | semi-truck with standard box trailer or flatbed |
Step 1: Vehicle Type
Select the vehicle that your autoduelist drives. Detailed below are the standard traits typically ascribed to each kind of vehicle. Since there is a tremendous amount of possible variation within each vehicle type, the stats reflect what is considered average. Spend points to alter the stats as you see fit. Some vehicles have innate advantages over others and are thus worth more points. Obviously, a more expensive vehicle leaves less points to buy modifications.
Motorcycles
Sports Bike
Cruiser/Touring Bike
[ +- ]
Examples:
Size:
Scale:
Chassis:
Suspension:
Tires:
Engine Type:
Engine Output:
Fuel Capacity:
Mileage Per Gallon:
Handling:
Acceleration:
Top Speed:
Toughness:
Crew:
Storage:
Special Features:
Flaws:
Weight:
Size:
Scale:
Chassis:
Suspension:
Tires:
Engine Type:
Engine Output:
Fuel Capacity:
Mileage Per Gallon:
Handling:
Acceleration:
Top Speed:
Toughness:
Crew:
Storage:
Special Features:
Flaws:
Weight:
Cruiser/Touring Bike
[ +- ]
Examples:
Size:
Scale:
Chassis:
Suspension:
Tires:
Engine Type:
Engine Output:
Fuel Capacity:
Mileage Per Gallon:
Handling:
Acceleration:
Top Speed:
Toughness:
Crew:
Storage:
Special Features:
Flaws:
Weight:
Size:
Scale:
Chassis:
Suspension:
Tires:
Engine Type:
Engine Output:
Fuel Capacity:
Mileage Per Gallon:
Handling:
Acceleration:
Top Speed:
Toughness:
Crew:
Storage:
Special Features:
Flaws:
Weight:
Trike
[ +- ]
Examples:
Size:
Scale:
Chassis:
Suspension:
Tires:
Engine Type:
Engine Output:
Fuel Capacity:
Mileage Per Gallon:
Handling:
Acceleration:
Top Speed:
Toughness:
Crew:
Storage:
Special Features:
Flaws:
Weight:
Size:
Scale:
Chassis:
Suspension:
Tires:
Engine Type:
Engine Output:
Fuel Capacity:
Mileage Per Gallon:
Handling:
Acceleration:
Top Speed:
Toughness:
Crew:
Storage:
Special Features:
Flaws:
Weight:
Passenger Cars & Light Trucks
Subcompact Car
Compact Car
Mid-Size Sedan or Coupe
Station Wagon
Luxury Car
Sports Car
Muscle Car
[ +- ]
Examples:
Size:
Scale:
Chassis:
Suspension:
Tires:
Engine Type:
Engine Output:
Fuel Capacity:
Mileage Per Gallon:
Handling:
Acceleration:
Top Speed:
Toughness:
Crew:
Storage:
Special Features:
Flaws:
Weight:
Size:
Scale:
Chassis:
Suspension:
Tires:
Engine Type:
Engine Output:
Fuel Capacity:
Mileage Per Gallon:
Handling:
Acceleration:
Top Speed:
Toughness:
Crew:
Storage:
Special Features:
Flaws:
Weight:
Compact Car
[ +- ]
Examples:
Size:
Scale:
Chassis:
Suspension:
Tires:
Engine Type:
Engine Output:
Fuel Capacity:
Mileage Per Gallon:
Handling:
Acceleration:
Top Speed:
Toughness:
Crew:
Storage:
Special Features:
Flaws:
Weight:
Size:
Scale:
Chassis:
Suspension:
Tires:
Engine Type:
Engine Output:
Fuel Capacity:
Mileage Per Gallon:
Handling:
Acceleration:
Top Speed:
Toughness:
Crew:
Storage:
Special Features:
Flaws:
Weight:
Mid-Size Sedan or Coupe
[ +- ]
Examples: Honda Accord, Nissan Sentra, Toyota Camry, Hyundai Elantra
Size: 3.
Scale: Normal.
Chassis: Any.
Suspension: Any.
Tires: Any.
Engine Type: Any.
Engine Output: Any, but usually Standard Output.
Fuel Capacity: 12 gallons.
Mileage Per Gallon: 28 (336 miles on a full tank).
Handling: +0
Acceleration: 60 mph per round.
Top Speed: 120 mph.
Toughness: 10 (2)
Crew: 1+4.
Storage: Roughly 16 cubic feet of trunk space.
Special Features: Basic Safety Features, Basic Amenities
Flaws: Any.
Weight: 3,000 lbs.
Size: 3.
Scale: Normal.
Chassis: Any.
Suspension: Any.
Tires: Any.
Engine Type: Any.
Engine Output: Any, but usually Standard Output.
Fuel Capacity: 12 gallons.
Mileage Per Gallon: 28 (336 miles on a full tank).
Handling: +0
Acceleration: 60 mph per round.
Top Speed: 120 mph.
Toughness: 10 (2)
Crew: 1+4.
Storage: Roughly 16 cubic feet of trunk space.
Special Features: Basic Safety Features, Basic Amenities
Flaws: Any.
Weight: 3,000 lbs.
Station Wagon
[ +- ]
Examples:
Size:
Scale:
Chassis:
Suspension:
Tires:
Engine Type:
Engine Output:
Fuel Capacity:
Mileage Per Gallon:
Handling:
Acceleration:
Top Speed:
Toughness:
Crew:
Storage:
Special Features:
Flaws:
Weight:
Size:
Scale:
Chassis:
Suspension:
Tires:
Engine Type:
Engine Output:
Fuel Capacity:
Mileage Per Gallon:
Handling:
Acceleration:
Top Speed:
Toughness:
Crew:
Storage:
Special Features:
Flaws:
Weight:
Luxury Car
[ +- ]
Examples:
Size:
Scale:
Chassis:
Suspension:
Tires:
Engine Type:
Engine Output:
Fuel Capacity:
Mileage Per Gallon:
Handling:
Acceleration:
Top Speed:
Toughness:
Crew:
Storage:
Special Features:
Flaws:
Weight:
Size:
Scale:
Chassis:
Suspension:
Tires:
Engine Type:
Engine Output:
Fuel Capacity:
Mileage Per Gallon:
Handling:
Acceleration:
Top Speed:
Toughness:
Crew:
Storage:
Special Features:
Flaws:
Weight:
Sports Car
[ +- ]
Examples:
Size:
Scale:
Chassis:
Suspension:
Tires:
Engine Type:
Engine Output:
Fuel Capacity:
Mileage Per Gallon:
Handling:
Acceleration:
Top Speed:
Toughness:
Crew:
Storage:
Special Features:
Flaws:
Weight:
Size:
Scale:
Chassis:
Suspension:
Tires:
Engine Type:
Engine Output:
Fuel Capacity:
Mileage Per Gallon:
Handling:
Acceleration:
Top Speed:
Toughness:
Crew:
Storage:
Special Features:
Flaws:
Weight:
Muscle Car
[ +- ]
Examples:
Size:
Scale:
Chassis:
Suspension:
Tires:
Engine Type:
Engine Output:
Fuel Capacity:
Mileage Per Gallon:
Handling:
Acceleration:
Top Speed:
Toughness:
Crew:
Storage:
Special Features:
Flaws:
Weight:
Size:
Scale:
Chassis:
Suspension:
Tires:
Engine Type:
Engine Output:
Fuel Capacity:
Mileage Per Gallon:
Handling:
Acceleration:
Top Speed:
Toughness:
Crew:
Storage:
Special Features:
Flaws:
Weight:
Jeep
Mid-Size Pick-Up Truck
Full-Size Pick-Up Truck
Sports Utility Vehicle
HMMWV (Hum-Vee)
Minivan
Van
[ +- ]
Examples:
Size:
Scale:
Chassis:
Suspension:
Tires:
Engine Type:
Engine Output:
Fuel Capacity:
Mileage Per Gallon:
Handling:
Acceleration:
Top Speed:
Toughness:
Crew:
Storage:
Special Features:
Flaws:
Weight:
Size:
Scale:
Chassis:
Suspension:
Tires:
Engine Type:
Engine Output:
Fuel Capacity:
Mileage Per Gallon:
Handling:
Acceleration:
Top Speed:
Toughness:
Crew:
Storage:
Special Features:
Flaws:
Weight:
Mid-Size Pick-Up Truck
[ +- ]
Examples:
Size:
Scale:
Chassis:
Suspension:
Tires:
Engine Type:
Engine Output:
Fuel Capacity:
Mileage Per Gallon:
Handling:
Acceleration:
Top Speed:
Toughness:
Crew:
Storage:
Special Features:
Flaws:
Weight:
Size:
Scale:
Chassis:
Suspension:
Tires:
Engine Type:
Engine Output:
Fuel Capacity:
Mileage Per Gallon:
Handling:
Acceleration:
Top Speed:
Toughness:
Crew:
Storage:
Special Features:
Flaws:
Weight:
Full-Size Pick-Up Truck
[ +- ]
Examples:
Size:
Scale:
Chassis:
Suspension:
Tires:
Engine Type:
Engine Output:
Fuel Capacity:
Mileage Per Gallon:
Handling:
Acceleration:
Top Speed:
Toughness:
Crew:
Storage:
Special Features:
Flaws:
Weight:
Size:
Scale:
Chassis:
Suspension:
Tires:
Engine Type:
Engine Output:
Fuel Capacity:
Mileage Per Gallon:
Handling:
Acceleration:
Top Speed:
Toughness:
Crew:
Storage:
Special Features:
Flaws:
Weight:
Sports Utility Vehicle
[ +- ]
Examples:
Size:
Scale:
Chassis:
Suspension:
Tires:
Engine Type:
Engine Output:
Fuel Capacity:
Mileage Per Gallon:
Handling:
Acceleration:
Top Speed:
Toughness:
Crew:
Storage:
Special Features:
Flaws:
Weight:
Size:
Scale:
Chassis:
Suspension:
Tires:
Engine Type:
Engine Output:
Fuel Capacity:
Mileage Per Gallon:
Handling:
Acceleration:
Top Speed:
Toughness:
Crew:
Storage:
Special Features:
Flaws:
Weight:
HMMWV (Hum-Vee)
[ +- ]
Examples:
Size:
Scale:
Chassis:
Suspension:
Tires:
Engine Type:
Engine Output:
Fuel Capacity:
Mileage Per Gallon:
Handling:
Acceleration:
Top Speed:
Toughness:
Crew:
Storage:
Special Features:
Flaws:
Weight:
Size:
Scale:
Chassis:
Suspension:
Tires:
Engine Type:
Engine Output:
Fuel Capacity:
Mileage Per Gallon:
Handling:
Acceleration:
Top Speed:
Toughness:
Crew:
Storage:
Special Features:
Flaws:
Weight:
Minivan
[ +- ]
Examples:
Size:
Scale:
Chassis:
Suspension:
Tires:
Engine Type:
Engine Output:
Fuel Capacity:
Mileage Per Gallon:
Handling:
Acceleration:
Top Speed:
Toughness:
Crew:
Storage:
Special Features:
Flaws:
Weight:
Size:
Scale:
Chassis:
Suspension:
Tires:
Engine Type:
Engine Output:
Fuel Capacity:
Mileage Per Gallon:
Handling:
Acceleration:
Top Speed:
Toughness:
Crew:
Storage:
Special Features:
Flaws:
Weight:
Van
[ +- ]
Examples:
Size:
Scale:
Chassis:
Suspension:
Tires:
Engine Type:
Engine Output:
Fuel Capacity:
Mileage Per Gallon:
Handling:
Acceleration:
Top Speed:
Toughness:
Crew:
Storage:
Special Features:
Flaws:
Weight:
Size:
Scale:
Chassis:
Suspension:
Tires:
Engine Type:
Engine Output:
Fuel Capacity:
Mileage Per Gallon:
Handling:
Acceleration:
Top Speed:
Toughness:
Crew:
Storage:
Special Features:
Flaws:
Weight:
Commercial Vehicles
Minibus
Bus: Public Transit
Bus: School
Bus: Double-Decker
[ +- ]
Examples:
Size:
Scale:
Chassis:
Suspension:
Tires:
Engine Type:
Engine Output:
Fuel Capacity:
Mileage Per Gallon:
Handling:
Acceleration:
Top Speed:
Toughness:
Crew:
Storage:
Special Features:
Flaws:
Weight:
Size:
Scale:
Chassis:
Suspension:
Tires:
Engine Type:
Engine Output:
Fuel Capacity:
Mileage Per Gallon:
Handling:
Acceleration:
Top Speed:
Toughness:
Crew:
Storage:
Special Features:
Flaws:
Weight:
Bus: Public Transit
[ +- ]
Examples:
Size:
Scale:
Chassis:
Suspension:
Tires:
Engine Type:
Engine Output:
Fuel Capacity:
Mileage Per Gallon:
Handling:
Acceleration:
Top Speed:
Toughness:
Crew:
Storage:
Special Features:
Flaws:
Weight:
Size:
Scale:
Chassis:
Suspension:
Tires:
Engine Type:
Engine Output:
Fuel Capacity:
Mileage Per Gallon:
Handling:
Acceleration:
Top Speed:
Toughness:
Crew:
Storage:
Special Features:
Flaws:
Weight:
Bus: School
[ +- ]
Examples:
Size:
Scale:
Chassis:
Suspension:
Tires:
Engine Type:
Engine Output:
Fuel Capacity:
Mileage Per Gallon:
Handling:
Acceleration:
Top Speed:
Toughness:
Crew:
Storage:
Special Features:
Flaws:
Weight:
Size:
Scale:
Chassis:
Suspension:
Tires:
Engine Type:
Engine Output:
Fuel Capacity:
Mileage Per Gallon:
Handling:
Acceleration:
Top Speed:
Toughness:
Crew:
Storage:
Special Features:
Flaws:
Weight:
Bus: Double-Decker
[ +- ]
Examples:
Size:
Scale:
Chassis:
Suspension:
Tires:
Engine Type:
Engine Output:
Fuel Capacity:
Mileage Per Gallon:
Handling:
Acceleration:
Top Speed:
Toughness:
Crew:
Storage:
Special Features:
Flaws:
Weight:
Size:
Scale:
Chassis:
Suspension:
Tires:
Engine Type:
Engine Output:
Fuel Capacity:
Mileage Per Gallon:
Handling:
Acceleration:
Top Speed:
Toughness:
Crew:
Storage:
Special Features:
Flaws:
Weight:
Big Rig (Tractor Only)
Recreational Vehicle (RV)
Box Truck
[ +- ]
Examples:
Size:
Scale:
Chassis:
Suspension:
Tires:
Engine Type:
Engine Output:
Fuel Capacity:
Mileage Per Gallon:
Handling:
Acceleration:
Top Speed:
Toughness:
Crew:
Storage:
Special Features:
Flaws:
Weight:
Size:
Scale:
Chassis:
Suspension:
Tires:
Engine Type:
Engine Output:
Fuel Capacity:
Mileage Per Gallon:
Handling:
Acceleration:
Top Speed:
Toughness:
Crew:
Storage:
Special Features:
Flaws:
Weight:
Recreational Vehicle (RV)
[ +- ]
Examples:
Size:
Scale:
Chassis:
Suspension:
Tires:
Engine Type:
Engine Output:
Fuel Capacity:
Mileage Per Gallon:
Handling:
Acceleration:
Top Speed:
Toughness:
Crew:
Storage:
Special Features:
Flaws:
Weight:
Size:
Scale:
Chassis:
Suspension:
Tires:
Engine Type:
Engine Output:
Fuel Capacity:
Mileage Per Gallon:
Handling:
Acceleration:
Top Speed:
Toughness:
Crew:
Storage:
Special Features:
Flaws:
Weight:
Box Truck
[ +- ]
Examples:
Size:
Scale:
Chassis:
Suspension:
Tires:
Engine Type:
Engine Output:
Fuel Capacity:
Mileage Per Gallon:
Handling:
Acceleration:
Top Speed:
Toughness:
Crew:
Storage:
Special Features:
Flaws:
Weight:
Size:
Scale:
Chassis:
Suspension:
Tires:
Engine Type:
Engine Output:
Fuel Capacity:
Mileage Per Gallon:
Handling:
Acceleration:
Top Speed:
Toughness:
Crew:
Storage:
Special Features:
Flaws:
Weight:
Emergency & Municipal Vehicles
Fire Truck
Garbage Truck
[ +- ]
Examples:
Size:
Scale:
Chassis:
Suspension:
Tires:
Engine Type:
Engine Output:
Fuel Capacity:
Mileage Per Gallon:
Handling:
Acceleration:
Top Speed:
Toughness:
Crew:
Storage:
Special Features:
Flaws:
Weight:
Size:
Scale:
Chassis:
Suspension:
Tires:
Engine Type:
Engine Output:
Fuel Capacity:
Mileage Per Gallon:
Handling:
Acceleration:
Top Speed:
Toughness:
Crew:
Storage:
Special Features:
Flaws:
Weight:
Garbage Truck
[ +- ]
Examples:
Size:
Scale:
Chassis:
Suspension:
Tires:
Engine Type:
Engine Output:
Fuel Capacity:
Mileage Per Gallon:
Handling:
Acceleration:
Top Speed:
Toughness:
Crew:
Storage:
Special Features:
Flaws:
Weight:
Size:
Scale:
Chassis:
Suspension:
Tires:
Engine Type:
Engine Output:
Fuel Capacity:
Mileage Per Gallon:
Handling:
Acceleration:
Top Speed:
Toughness:
Crew:
Storage:
Special Features:
Flaws:
Weight:
Ambulance
Police Car
[ +- ]
Examples:
Size:
Scale:
Chassis:
Suspension:
Tires:
Engine Type:
Engine Output:
Fuel Capacity:
Mileage Per Gallon:
Handling:
Acceleration:
Top Speed:
Toughness:
Crew:
Storage:
Special Features:
Flaws:
Weight:
Size:
Scale:
Chassis:
Suspension:
Tires:
Engine Type:
Engine Output:
Fuel Capacity:
Mileage Per Gallon:
Handling:
Acceleration:
Top Speed:
Toughness:
Crew:
Storage:
Special Features:
Flaws:
Weight:
Police Car
[ +- ]
Examples:
Size:
Scale:
Chassis:
Suspension:
Tires:
Engine Type:
Engine Output:
Fuel Capacity:
Mileage Per Gallon:
Handling:
Acceleration:
Top Speed:
Toughness:
Crew:
Storage:
Special Features:
Flaws:
Weight:
Size:
Scale:
Chassis:
Suspension:
Tires:
Engine Type:
Engine Output:
Fuel Capacity:
Mileage Per Gallon:
Handling:
Acceleration:
Top Speed:
Toughness:
Crew:
Storage:
Special Features:
Flaws:
Weight:
Miscellaneous
Buggy
Stretch Limousine
Hearse
[ +- ]
Examples:
Size:
Scale:
Chassis:
Suspension:
Tires:
Engine Type:
Engine Output:
Fuel Capacity:
Mileage Per Gallon:
Handling:
Acceleration:
Top Speed:
Toughness:
Crew:
Storage:
Special Features:
Flaws:
Weight:
Size:
Scale:
Chassis:
Suspension:
Tires:
Engine Type:
Engine Output:
Fuel Capacity:
Mileage Per Gallon:
Handling:
Acceleration:
Top Speed:
Toughness:
Crew:
Storage:
Special Features:
Flaws:
Weight:
Stretch Limousine
[ +- ]
Examples:
Size:
Scale:
Chassis:
Suspension:
Tires:
Engine Type:
Engine Output:
Fuel Capacity:
Mileage Per Gallon:
Handling:
Acceleration:
Top Speed:
Toughness:
Crew:
Storage:
Special Features:
Flaws:
Weight:
Size:
Scale:
Chassis:
Suspension:
Tires:
Engine Type:
Engine Output:
Fuel Capacity:
Mileage Per Gallon:
Handling:
Acceleration:
Top Speed:
Toughness:
Crew:
Storage:
Special Features:
Flaws:
Weight:
Hearse
[ +- ]
Examples:
Size:
Scale:
Chassis:
Suspension:
Tires:
Engine Type:
Engine Output:
Fuel Capacity:
Mileage Per Gallon:
Handling:
Acceleration:
Top Speed:
Toughness:
Crew:
Storage:
Special Features:
Flaws:
Weight:
Size:
Scale:
Chassis:
Suspension:
Tires:
Engine Type:
Engine Output:
Fuel Capacity:
Mileage Per Gallon:
Handling:
Acceleration:
Top Speed:
Toughness:
Crew:
Storage:
Special Features:
Flaws:
Weight:
Food Truck/Ice Cream Truck
Monster Truck
Golf Cart
[ +- ]
Examples:
Size:
Scale:
Chassis:
Suspension:
Tires:
Engine Type:
Engine Output:
Fuel Capacity:
Mileage Per Gallon:
Handling:
Acceleration:
Top Speed:
Toughness:
Crew:
Storage:
Special Features:
Flaws:
Weight:
Size:
Scale:
Chassis:
Suspension:
Tires:
Engine Type:
Engine Output:
Fuel Capacity:
Mileage Per Gallon:
Handling:
Acceleration:
Top Speed:
Toughness:
Crew:
Storage:
Special Features:
Flaws:
Weight:
Monster Truck
[ +- ]
Examples:
Size:
Scale:
Chassis:
Suspension:
Tires:
Engine Type:
Engine Output:
Fuel Capacity:
Mileage Per Gallon:
Handling:
Acceleration:
Top Speed:
Toughness:
Crew:
Storage:
Special Features:
Flaws:
Weight:
Size:
Scale:
Chassis:
Suspension:
Tires:
Engine Type:
Engine Output:
Fuel Capacity:
Mileage Per Gallon:
Handling:
Acceleration:
Top Speed:
Toughness:
Crew:
Storage:
Special Features:
Flaws:
Weight:
Golf Cart
[ +- ]
Examples:
Size:
Scale:
Chassis:
Suspension:
Tires:
Engine Type:
Engine Output:
Fuel Capacity:
Mileage Per Gallon:
Handling:
Acceleration:
Top Speed:
Toughness:
Crew:
Storage:
Special Features:
Flaws:
Weight:
Size:
Scale:
Chassis:
Suspension:
Tires:
Engine Type:
Engine Output:
Fuel Capacity:
Mileage Per Gallon:
Handling:
Acceleration:
Top Speed:
Toughness:
Crew:
Storage:
Special Features:
Flaws:
Weight:
Step 2: Chassis
Standard:
Light:
Reinforced:
Extra Reinforced:
Step 3: Suspension
Standard:
Racing Suspension:
Off-Road Suspension:
Active Suspension:
Step 4: Tires
Standard:
Off-Road Tires:
Racing Slicks:
Run Flat Tires:
Airless Tires:
Huge Tires:
Step 5: Engine Type
The engine, or power plant, is the heart of the vehicle. It provides the power necessary to make the vehicle move. Among autoduelists, gasoline is king. This is followed closely by diesel engines, but electric motors are not far behind. As battery technology continues to improve, EVs have become more and more commonplace in the arenas.
Select one Engine Type from the options below. Your engine determines the fuel that your vehicle consumes.
[ +- ] Internal Combustion Engine: Gasoline (0 Points)
The most common engine of the 20th and 21st centuries. This engine type uses gasoline, everyone's favorite flammable hydrocarbons, to generate the power needed to propel the vehicle. Within the engine's combustion chamber, a mixture of gasoline and air is burned. The expansion of heated gases works a piston in a cylinder that drives a crankshaft, providing the rotary action needed to turn the wheels.
[ +- ] Internal Combustion Engine: Diesel (0 Points)
[ +- ] Internal Combustion Engine: Methanol (1 Point)
[ +- ] Internal Combustion Engine: Multifuel (2 Points)
This is an internal combustion engine designed to run on a select range of fuels. Fuel security and flexibility are the main reasons one chooses this power plant. Multifuel vehicles are convenient for emergency situations where traditional gasoline and diesel are unavailable. Autodueling events in which fuel supply is a factor, such as cannonball runs or endurance racing, are the kinds of competitions where these machines stand out.
There are two varieties of multifuel engine:
◆ A gasoline multifuel engine can run on low or high octane gasoline and any petroleum fuels that are spark ignited. This includes methanol, LPG (liquified petroleum gas), and various ethanol blends.
◆ A diesel multifuel engine can run on low or high cetane diesel and any petroleum fuels that are compression ignited. This includes kerosene, certain kinds of jet fuel, and even cooking and heating oil.
Multifuel engines tend to suffer underperformance issues due to the design compromises necessary to combust multiple fuels in the same engine. Being able to burn a plurality of fuels means not being able to burn any single fuel very efficiently. Thus, fuel consumption is somewhat high compared to other engine types of similar size and output. When running on its primary fuel (gas or diesel), a multifuel appliance experiences no loss of performance (i.e., no penalties). When the engine employs one of its accepted alternative fuels, however, there is an immediate reduction in power and efficiency. Reduce top speed and acceleration by 10% (round up).
A multifuel vehicle is typically equipped with two fuel tanks. One tank holds the primary fuel, while the other tank is intended for any alternative fuels. The driver can manually switch back and forth between both tanks. The price of the second tank has been factored into the point cost for the engine.
[ +- ] Internal Combustion Engine: Alternative Fuel (-1 Points)
-- Ethanol
-- Liquified Natural Gas
-- Compressed Natural Gas
-- Biogas
[ +- ] Electric Motor (2 Points)
A vehicle with an electric motor operates exclusively on electricity instead of liquid fuel. The electricity is provided by way of a sophisticated high voltage battery or fuel cell.
Electric vehicles (EVs) have many advantages. Also, due to the lack of noisy mechanical parts, electric motors run much quieter than internal combustion engines, especially at low speeds.
However, electric motors also have their drawbacks. Mileage is an example. Generally speaking, an electric vehicle doesn't get the same amount of miles from a fully-charged battery that a gas- or diesel-powered vehicle does from a full fuel tank (this will change in the near future as battery technology improves, but presently that's the case). Another issue is recharge time. An internal combustion vehicle can be fully refueled in minutes, whereas an electric vehicle needs hours to fully recharge. Even using the fastest charging stations available, an EV battery requires a minimum of 20 minutes to reach a full charge. As a result, EVs are not well-suited for long-distance races. For such events, most autoduelists forgo electric vehicles in favor of their internal combustion counterparts.
Use the table below to determine how long it takes to fully charge a vehicular electric battery. Vehicles with larger battery capacities will obviously take more time to reach a full charge. Typically, an EV driver will charge their vehicle when the battery drops to 10-20%. If the car is equipped with a regenerative braking system, then the battery is usually only charged up to 80%, leaving room for the brakes to top it off.
| Charging Station | Recharge Rate | Time to Fully Charge a 40 kWh Battery |
| Level 1 | 1 kW | 40 hours |
| Level 2 | 10 kW | 4 hours |
| Level 3 (Fast-Charging) | 100 to 300 kW | 24 min. to 8 min. |
[ +- ] Hybrid Engine (1 Point)
Step 6: Engine Output
Output is an abstract measure of the vehicle’s horsepower, torque, and RPMs. In other words, it is a measure of how hard the engine works and how rapidly it does that work. In internal combustion engines, output represents a variety of engine characteristics, such as cylinder number and configuration, internal displacement, air intake, valve timing, and the engine's overall tuning, among other things. In electric motors, it alludes to the motor's size, efficiency rating, and voltage.
Output plays a part in determining the vehicle's top speed, as well as how quickly it can accelerate. For the sake of simplicity, output is separated into three categories: Standard, Improved, and High. Note that these categories are relative to each vehicle. What is considered "high output" for a car engine might qualify as merely "standard output" for a big rig's engine.
Select the desired type of output for your vehicle.
Standard Output: This is engine is
Improved Output:
High Output: A high output engine is the most sophisticated power plant available for that vehicle type. This is your classic "high performance" engine. A vehicle with this kind of power plant possesses superior horsepower and torque in comparison to other vehicles of the same type.
High output engines are demanding pieces of machinery. They require a significant amount of maintenance and costly replacement parts. Those with internal combustion engines also need specialized coolants, cleaners, and motor oil. All of this can make upkeep prohibitively expensive. Still, many autoduelists consider these powerful engines worth the extra work and expense. For those who participate in AADA racing events (e.g., "death races"), high output engines are often regarded as a necessity in order to stay competitive.
[size=115]
Fuel Grades
Specialty methanol or high octane gasoline to function at optimal levels. The use of low octane fuel results in diminished engine efficiency (reduce top speed and acceleration by 10%) and risks doing severe damage to the engine's inner workings.
Output-to-Weight Ratio
| Vehicle Type | Low Output | Medium Output | High Output |
| Subcompact Car | |||
| Compact Car | |||
| Sedan/Coupe | |||
| Station Wagon | |||
| Luxury Car | |||
| Sports Car | |||
| Muscle Car | |||
| Jeep | |||
| Sports Utility Vehicle | |||
| HMMWV (Hum-Vee) | |||
| Van | |||
| Pick-Up Truck | |||
| Box Truck | |||
| Stretch Limousine | |||
| Hearse | |||
| Motorcycle: Sports Bike | |||
| Motorcycle: Cruiser/Touring Bike | |||
| Motorcycle: Trike | |||
| Minibus | |||
| Bus: Public Transit | |||
| Bus: School | |||
| Bus: Double-Decker | |||
| Big Rig (Tractor Only) | |||
| Recreational Vehicle (RV) | |||
| Fire Truck | |||
| Garbage Truck | |||
| Food Truck/Ice Cream Truck | |||
| Ambulance | |||
| Monster Truck |
Step 7: Armor
Step 8: Armaments
Mount Types
Fixed Mount:
Pintle Mount:
Ring Mount:
Articulated Mount:
Hardpoint:
Fire Controls
Manned:
Remote:
Automated:
Close Combat Weaponry
| Weapon | Range | Damage | AP | RoF | Shots | Weight | Mount | Mods |
| Ram Prow | ||||||||
| Wheel Blades |
Ranged Weaponry
| Weapon | Range | Damage | AP | RoF | Shots | Weight | Mount | Mods |
| Light Machinegun | ||||||||
| Medium Machinegun | ||||||||
| Heavy Machinegun | ||||||||
| Chain Gun | ||||||||
| Minigun (7.62 mm) | ||||||||
| Autocannon | ||||||||
| Grenade Launcher | ||||||||
| Rocket Launcher | ||||||||
| Net Launcher | ||||||||
| Flame Thrower | ||||||||
| Harpoon Gun w/ Winch & Line |
Dropped Weapons
Dropped weapons work on the premise that it is easier to take out an opponent by making him crash than shooting him up. They either cause crashes by damaging tires (mines or spikes) or causing a loss of control or visibility (oil, paint or smoke). Dropped weapons are simple and effective. Their drawbacks are that they are short-ranged and indiscriminate, attacking friend or foe. They are also useless if your enemy is in front of you, which means a person relying on dropped weapons should have a fast car. They are popular, not just with autoduelists, but with anyone wanting to discourage pursuit without resorting to gunplay.
| Weapon | Range | Damage | AP | RoF | Shots | Weight | Mount | Mods |
| ADW Dispenser | ||||||||
| Block Dropper | ||||||||
| Mine Dropper | ||||||||
| Road Strip Ejector |
Step 9: Special Features
Performance
| Feature | Mods | Description |
| 90-Degree Wheel Rotation | ||
| 4-Wheel Drive | ||
| Active Suspension | ||
| Air Dam | ||
| Airbrakes | ||
| Alternative Engine Placement | ||
| Drive-By-Wire System | ||
| Heavy-Duty Shocks | ||
| High Performance Brakes | ||
| Increased Battery Capacity | ||
| Increased Fuel Efficiency | ||
| Increased Horsepower | ||
| Increased Torque | ||
| Independently Rotating Wheels | ||
| Nitrous Oxide | ||
| Regenerative Braking System | ||
| Short Throw Shifter | ||
| Spoiler | ||
| Supercharger | ||
| Turbocharger |
Offense
| Feature | Mods | Description |
| Extra Fire Controls | ||
| Grapnel Launcher and Towline | ||
| Gun Cover | ||
| Gun Port | ||
| Oil Slick Sprayer | ||
| Paint Sprayer | ||
| Ram Plate | ||
| Remote Trigger System | ||
| Road Strip Ejector | ||
| Smoke Dispenser | ||
| Weapon Emplacement | ||
| Wheel Blades |
Security & Defense
| Feature | Mods | Description |
| Alarm | ||
| Automatic Detainment System | ||
| Biometric Ignition | ||
| Brake Locks | ||
| Bullet-Proof Windows | ||
| Keypad Entry | ||
| Killswitch | ||
| Partition Cage | ||
| Steering Wheel Lock | ||
| Wheel Guard |
Sensors & Instruments
| Feature | Mods | Description |
| Cameras | ||
| CB Radio | ||
| Gun Cam | ||
| GPS | ||
| Heads-Up Display | ||
| Improved Instrumentation | ||
| Nightvision | The vehicle uses nightvision optics to assist the driver in seeing clearly in dark conditions. Nighttime autoduels can often take place in locales with little to no street lights, which leaves many drivers struggling to see in the dark. The enhanced video is displayed on a dashboard screen or projected onto the windshield. |
Utility
| Feature | Mods | Description |
| Amenities, Basic | This covers non-essential features that are standard in modern vehicles. This usually includes the following: cup holders, air conditioning, radio and speaker system, bluetooth connectivity, power windows, one or more auxiliary power outlets, etc. | |
| Amenities, Luxury | A step up from basic amenities, this includes high-end non-essential features such as heated seats, leather interior, satellite radio, top-notch speaker system, touchscreen interfaces, in-car WiFi, and video screens built into the center console and headrests, among many other possibilities. | |
| Bullbar | ||
| Extra Entry/Exit Points | ||
| Hitch | ||
| Loudspeaker | ||
| Motorized Winch | ||
| Spotlight |
Safety
| Feature | Mods | Description |
| 5-Point Harness | ||
| Ejection Seat | ||
| Fire Extinguisher | ||
| Fire Suppression System | ||
| Roll Cage | ||
| Standard Safety Features | 0 | This covers basic equipment designed to improve the safety and crash survivability of a vehicle's occupants. It includes seatbelts, front airbags, shatterproof glass, windshield wipers, child safety locks, anti-lock brakes, and various driver assist systems. Some vehicles are further equipped with side airbags, a release latch in the trunk, and a backup camera. Most of these features are mandated by U.S. law, and so they are standard in nearly all modern passenger and commercial automobiles. |
Miscellaneous
| Feature | Mods | Description |
| Camper Trailer | ||
| Concealed Compartment | ||
| Cosmetic Modifications | ||
| Dozer Blade | ||
| Extra Manual Controls | ||
| Extra Seats | ||
| Hand Controls | ||
| One-Way Window Tint | ||
| Self-Sealing Fuel Tank | ||
| Semi-Trailier: Box | ||
| Semi-Trailer: Car Hauler | ||
| Semi-Trailer: Flatbed | ||
| Semi-Trailer: Tanker | ||
| Sidecar |
Step 10: Flaws
| Feature | Mods | Description |
| Missing Safety Features | -2/-1 | The vehicle is not equipped with the standard safety measures found in most cars and trucks. This includes basics such as seat belts, airbags, anti-lock brakes, and more. Motorcycles are considered to have a reduced version of this flaw (-1 point); they aren't equipped with seatbelts but do possess some safety equipment. Note that this flaw is almost always accompanied by the Not Street Legal flaw, since safety features are required in order to be street legal. |
| Not Street Legal | -1 | The vehicle is not legally permitted to operate on public streets. This is typically the case when a vehicle does not meet the mandated criteria for lighting, signal lights, and safety equipment. It might also be as simple as the registration and/or inspection sticker being expired. Using such a vehicle on a public roadway may result in legal consequences for the driver, including fines and impoundment of said vehicle. This flaw is common for vehicles restricted to specific off-road operating areas. Examples include ATVs, golf carts, dune buggies, motorized construction equipment, and farming machinery. Likewise, race cars are intended for use on a closed track and therefore don't always meet the requirements of a street-legal vehicle. With the right modifications, however, most conveyances not designed for on-road driving can be adapted for street use. |
0.8 horsepower per cubic inch
1 cubic inch equals 0.0163871 liters
1 liter equals 61.0237 cubic inches
Sedan = 1.5 liter/91.5356 cubic inches/1,500cc engine = 73.6
50-350 kWh
2013 Honda Civic LX
Displacement: 1.8 liters / 109.843 cubic inches / 1,800cc
Horsepower: 140 hp @ 6,500 rpm / 88 hp
Mileage: 28/39 (city/highway)
Horsepower
Power to Weight Ratio
-- 20 lbs:1 HP regular
--10 lbs.:1 HP mild performance
--8 lbs:1Hp high performance